Fortigate and Linux: Creating a Secure GRE over IPSEC Tunnel
Introduction
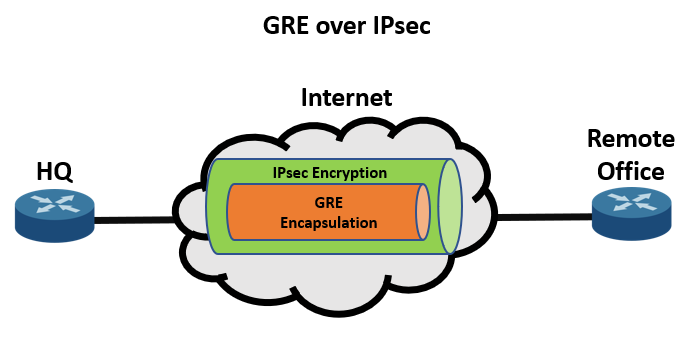
In today’s network environments, secure and efficient communication between remote sites is critical. A popular solution for achieving this is by configuring a GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) tunnel over an IPSEC (Internet Protocol Security) tunnel. GRE provides a way to encapsulate various network layer protocols, while IPSEC ensures that the traffic passing through the tunnel is encrypted and secure.
This guide covers configuring a GRE over IPSEC tunnel between a Fortigate firewall and a Linux server, combining the flexibility of GRE for encapsulating traffic with the encryption of IPSEC. Additionally, it explores an optional policy-based route to control traffic flow through the tunnel. By the end, you'll have a secure and efficient connection between the Fortigate and Linux server for encrypted data exchange.
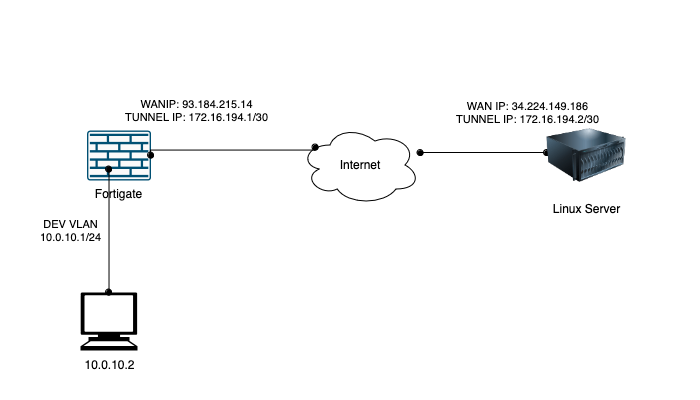
Example Topology:
Stage 1: Linux Sever
Update Repository
sudo apt-get update
Install Strongswan
sudo apt install strongswan strongswan-pki libcharon-extra-plugins \
libcharon-extauth-plugins libstrongswan-extra-plugins libtss2-tcti-tabrmd0 -y
Start and enable the service:
systemctl enable --now strongswan-starter.service
Enable packet forwarding in /etc/sysctl.conf. I would backup the file first.
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1
net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0
net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0
Apply changes:
sysctl -p
Configure the StrongSwan file in /etc/ipsec.confI would backup the file first too.
# ipsec.conf - strongSwan IPsec configuration file
# basic configuration
config setup
# strictcrlpolicy=yes
uniqueids = yes
charondebug= "all"
# Add connections here.
conn strongswan-to-fortigate
type = tunnel
auto = start
keyexchange = ikev2
authby = secret
#leftid = %any
left = 34.224.149.186
leftsubnet = 0.0.0.0/0
rightid = %any
right = 93.184.215.14
rightsubnet = 10.0.10.0/24
ike = aes256-sha256-modp2048
esp = aes256-sha256-modp2048
aggressive = no
keyingtries = %forever
ikelifetime = 28800s
lifetime = 3600s
dpddelay = 20s
dpdtimeout = 120s
dpdaction = restart
## add extra remote subnets
conn tunnel
also=strongswan-to-fortigate
rightsubnet = 172.16.194/30
Create authentication and access secrets. in /etc/ipsec.secrets
# This file holds shared secrets or RSA private keys for authentication.
# RSA private key for this host, authenticating it to any other host
# which knows the public part.
34.224.149.186 93.184.215.14 : PSK "passwordStrongAF"
Configure Tunnel interface
ip tunnel add vti0 local 34.224.149.186 remote 93.184.215.14 mode vti key 12
ip link set up dev vti0
ip addr add 172.16.194.2/30 remote 172.16.194.1/30 dev vti0
# Below are the subnets on the other end that we will route via the tunnel
ip route add 10.0.10.0/24 via 172.16.194.1 dev vti0
ip route add 172.16.194.2/30 via 172.16.194.1 dev vti0
Restart Strongswan
ipsec restart
ipsec status
Stage 2: Configure Fortigate
Configure Phase 1
config vpn ipsec phase1-interface
edit "TO-LINUX-SERVER"
set interface "wan1"
set ike-version 2
set keylife 28800
set peertype any
set net-device disable
set proposal aes256-sha256
set remote-gw 93.184.215.14
set psksecret ENC passwordStrongAF
next
end
Configure Phase 2:
config vpn ipsec phase2-interface
edit "TO-LINUX-SERVER"
set phase1name "TO-LINUX-SERVER"
set proposal aes256-sha256
set keylifeseconds 3596
set src-subnet 10.0.10.0 255.255.255.0
set dst-subnet 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
next
edit TO-LINUX-TUNNEL
set phase1name "TO-LINUX-SERVER"
set proposal aes256-sha256
set keylifeseconds 3596
set src-subnet 172.16.194.0 255.255.255.252
set dst-subnet 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
end
Tunnel Interface
config system interface
edit "FG-TO-CLOUD"
set vdom "root"
set ip 172.16.194.1 255.255.255.255
set allowaccess ping
set type tunnel
set remote-ip 172.16.194.2 255.255.255.252
set snmp-index 30
set interface "wan1"
set mtu-override enable
set mtu 1480
next
end
Static Route on FG to point to tunnel:
config router static
edit 3
set dst 172.16.194.0 255.255.255.252
set device "FG-TO-CLOUD"
set link-monitor-exempt enable
next
Stage 3: Linux Server Firewall, NATTING and MTU/MSS
If you want to route "Internet" bound traffic from Fortigate through to th Linux Sever, you need to configure the Linux server to Route and SNAT/SPAT. To achieve this, you need to amment the IP Tables Rules on the Strongswan Server:
To set a linux machine as a router you need the following
1- Enable forwarding on the box with
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Assuming your public interface is eth1 and local interface is eth0
2- Set the natting rule with:
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth1 -j MASQUERADE
3- Accept traffic from eth0:
iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -j ACCEPT
4- Allow established connections from the public interface.
iptables -A INPUT -i eth1 -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
5- Allow outgoing connections:
iptables -A OUTPUT -j ACCEPT
If you encounter MTU/MSS issues, you can deal with them with:
Add these lines
iptables -t mangle -A FORWARD -m policy --pol ipsec --dir in -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN -m tcpmss --mss 1361:1536 -j TCPMSS --set-mss 1360
iptables -t mangle -A FORWARD -m policy --pol ipsec --dir out -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN -m tcpmss --mss 1361:1536 -j TCPMSS --set-mss 1360
Policy Route (optional)
The last part is to create a policy map that routes all 10.0.10.2 traffic, though the tunnel.
config router policy
edit 1
set input-device "Dev-VLAN"
set src "10.0.10.2/255.255.255.255"
set dst "0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0"
set gateway 172.16.196.2
set output-device "TO-LINUX-SERVER"
next
end
