Bulding a weather station with a Raspberry Pi
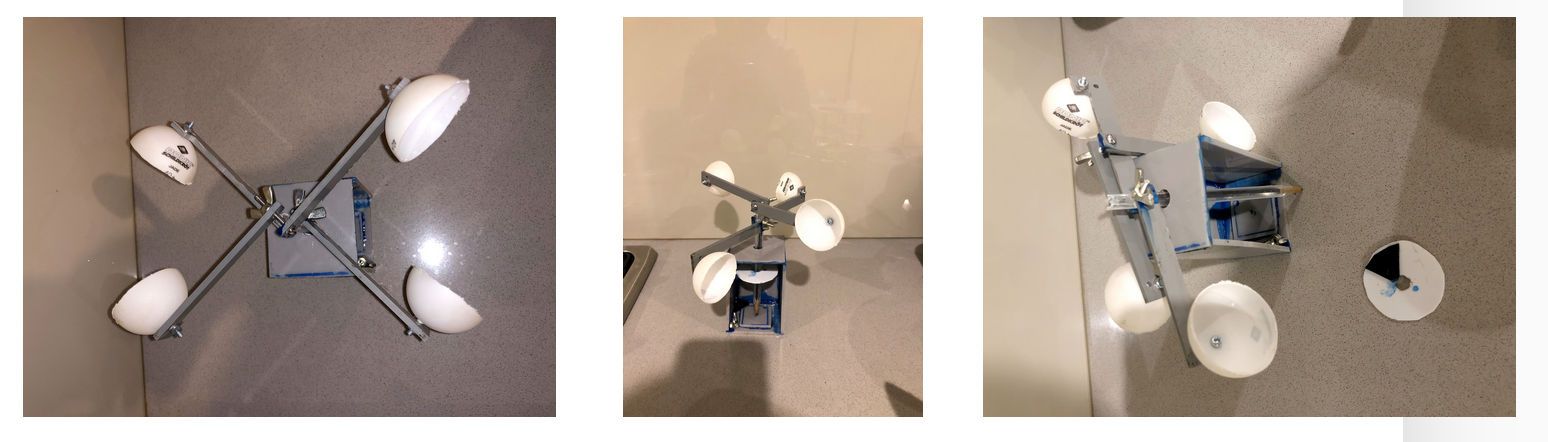
What you need
- Reflective IR Sensor with 470 and 10K Resistors
- DHT11 Temperature and Relative Humidity Sensor Module
- Ping Pong Balls
- Screws
- PVC Plastic sheets
- Raspberry Pi
Build It

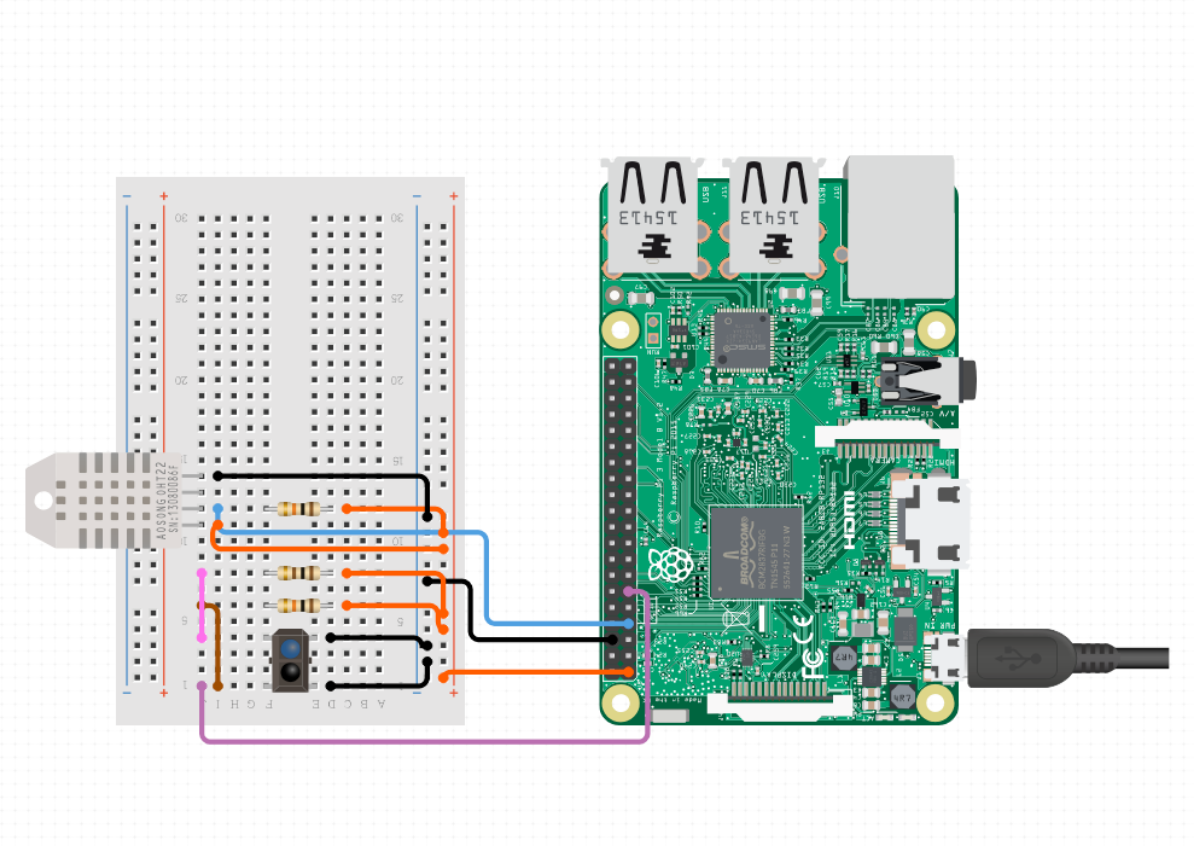
Wiring Schematic
I ended up soldering male pins onto the end 2 ethernet cables, then plugging both the temp sensor and ir sensor on the end of those ethernet cable.
i then placed ensembled them into the housing, put the whole thing outside
Code (with comments)
# Import Libraries
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import Adafruit_DHT as DHT
# workbook, check that this library is still supported though
from openpyxl import load_workbook
import math
# Time Variables
import time
from time import sleep, strftime
import datetime
from datetime import date
# initialise Pins
DHT_PIN = #Define DHT Pin Sensor
PHOTOTRANSISTOR_SENSOR_PIN = # Define IR Sensor Pin, This is the sesor Pin and NOT THE Transmitor/ Link to Sensor: https://www.adafruit.com/product/2349
dht = DHT.DHT(DHT_PIN)
# Pinout config, i prefer BCM mode but you could always go for "BOARD"
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(PHOTOTRANSISTOR_SENSOR_PIN,GPIO.IN)
# Load Workbook
wb = load_workbook('/DEFINE/ABSOLUTE/PATH_TO_SHEET')
sheet = wb['Sheet1'] # Sheet number is important
# Set Diameter which is measured from Propeller to Proppelry in mm
vane_diameter = float(106)
# Calculates the circumfrance of the arc in meters
vane_circ = float (vane_diameter/1000)*math.pi
# this accounts for the inevitable ineffeciancy of the anemometer, Anonometers are actually very interesting, Link for more: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4279541/#:~:text=Cup%20anemometer%20factor%2C%20K%20(defined,sketch%20on%20the%20right%20side).
afactor = float(2.5)
print('Measuring wind speed...')
#time
try:
while True:
# read values from the DHT11 sensor
temp = dht.temperature
humdity = dht.humidity
today = date.today()
now = datetime.datetime.now().time()
TEST_TIME = # Define the length of time, in seocnds that the program should run for
# Measuring the Wind Speed
sensorstart = GPIO.input(PHOTOTRANSISTOR_SENSOR_PIN)
rotations = float(0)
trigger = 0
endtime = time.time() + TEST_TIME
# loop for the duration of TEST_TIME, in seconds
while time.time() < endtime:
# records whenever the Phototranistor hits the white refelective strip. but will only do so if the strip has moved
if GPIO.input(PHOTOTRANSISTOR_SENSOR_PIN)==1 and trigger==0:
rotations = rotations + 1
# This basically stores the curent state of the trigger, which stops the incriment of Rotation, in the case that
# the rotating plastic hasnt moved between now and the next loop.
trigger=1
if GPIO.input(PHOTOTRANSISTOR_SENSOR_PIN)==0:
trigger = 0
#this timer avoids a perculiar issue where the sensors return a garbage reading if read right away.
time.sleep(0.001)
# handle posible sensor error
if rotations==1 and sensorstart==1:
rotations = 0
ROTATIONS_PER_SECOND = float(rotations/10)
# calculates the wind speed
windspeed = float((ROTATIONS_PER_SECOND)*vane_circ*afactor)
print('{:.0f} rotations = {:.2f} rotations/second'.format(rotations, rotations/10))
print('Windspeed is {:.2f} m/s'.format(windspeed))
# adds data to the spreedsheet. ITS IMPORTANT THE THE VARIBLES NAMES MATCH THE ROW TITLES ON THE SPREESHEET
row = (today, now, temp, humdity, windspeed)
sheet.append(row)
wb.save('/DEFINE/ABSOLUTE/PATH_TO_SHEET')
print("Data added to sheet and SAVED!!!!!")
sleep(10)
finally:
# Save it if something goes wrong loool
wb.save('ABSOLUTE_PATH_TO_SHEET')
print('*Waves* Goodbye, haha get it?? WAVE??? because the motion of a hand wave would also create a bit of... wind?? haha damnnn yea anyway the weather is nuts huh' )
